|
|
Project settings
How to change the video's resolution
You can adjust the parameters of your video, such as bitrate, video resolution and frame rate. These settings affect the quality and the size of a final file. You can change them when saving your video or at any other time.
Opening project settings
In the Export window click the Advanced button.
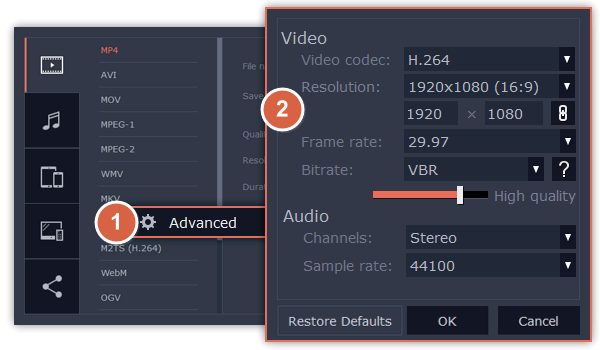
Video settings
The video settings apply to all videos and photos used in the project.
Resolution
The frame size or resolution determines the videos width and height in pixels. Open the Frame Size list to select from the most common resolutions. For your convenience, each resolution is marked with its respective aspect ratio. Ideally, the frame size should match the resolution of the videos and photos you plan to use in your project, and should not exceed the resolution of the largest video. Smaller resolutions allow you to make the output video smaller and thus save your disc space, however, this will sacrifice some video quality due to downscaling.
|
Frame Size
|
Aspect Ratio
|
|
320x240
|
4:3
|
|
640x480
|
4:3
|
|
1280x720
|
16:9
|
|
1280x960
|
4:3
|
|
1920x1080
|
16:9
|
|
1920x1440
|
4:3
|
|
3840х2160
|
16:9
|
|
4096х2160
|
256:135
|
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio is the ratio of the video or photo's width to its height. The most commonly used aspect ratios are 4:3, used generally for analog TV and in many old movies, and 16:9, the standard resolution for widescreen digital video.
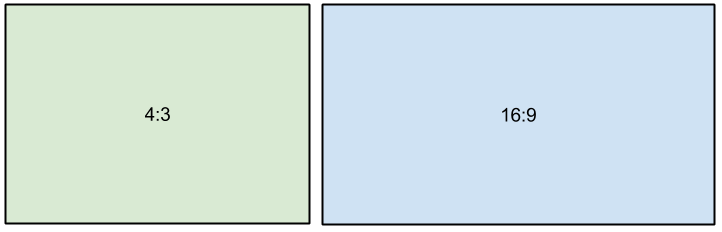
A relative comparison of aspect ratios
When you add videos and photos to the project, they will be scaled to fit the specified frame size. If you add media files with an aspect ratio different from that of the project, you may see black bars appear on the sides of the video. Furthermore, if you add low-quality videos to a project set up to a high resolution (frame size), the small video may be stretched to fit the frame and thus may appear pixellized. For best results, we recommend setting the frame size and aspect ratio to match all or most of the videos and photos you are planning to use.
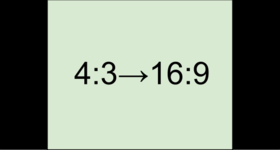

Examples of black bars appearing when importing videos with a different aspect ratio.
If you cannot find the necessary frame size in the list, you can manually enter the width and height into the respective boxes of the Project Settings window. Note the button with the link icon to the right of the boxes. It allows you to maintain existing proportions when entering new values:  – the proportions are constrained, allowing you to set a larger or smaller frame size without changing the aspect ratio;
– the proportions are constrained, allowing you to set a larger or smaller frame size without changing the aspect ratio;  – you can freely enter the width and height with any proportions. Simply click this button to toggle the two states.
– you can freely enter the width and height with any proportions. Simply click this button to toggle the two states.
Frame rate
Frame rate or FPS defines the frequency at which frames appear on a display per second. Frame rate affects the smoothness of the video being played. Standard frame rate in most types of videos is 24-30 frames per second. The video plays smoother at a higher value, but the file size rises as well.
Bitrate
Bitrate is the amount of digital information contained in one second of a media file. It is measured in kilobits per second (Kbps). You can control the output file size by changing the bitrate value. There are three types of bitrate available in the video editor:
Auto bitrate (CBR) is a constant value set by the program and calculated according to other already set quality options such as video codec, resolution and frame rate.
Constant bitrate (custom CBR) is a constant manually entered value which is then used to process the entire video. This type of bitrate allows to predict the size of a final media file.
Variable bitrate (VBR) is an automatically picked value that is set within the set quality requirements for the video. VBR will adjust to the image using the optimal values to save the quality: lower values for a static image and higher values for a more dynamic one. But in this case it is impossible to predict the output file size.
Audio settings
Sample rate
The sample rate affects the quality of digital sound, and defines the maximum frequencies that an audio stream can contain. The default sample rate is set to 44100 Hz, which exceeds the maximum frequencies of human hearing and is used to record Audio CDs and most music tracks.
Channels
Stereo sound contains two channels and has the capacity to convey the relative location of sound sources, which makes it best for recording music; mono sound has only one channel and produces sound without differentiating left and right channels. Stereo is the generally preferred number of channels, however, some mobile devices record sound only in mono mode.
Surround sound (5.1) has the capacity to produce sound using six channels (usually 5 speakers and a subwoofer), which allows it to create the so called participation effect. This technology is often used in home cinema systems, as well as in some game consoles and PCs.
See also: