|
|
Glossary
Here's a list of some terms that you may come across while working with video and audio. You won't need to know all of these to use Movavi software, but if you want to learn more about the specifics of media file processing, you can start here.
Aspect ratio
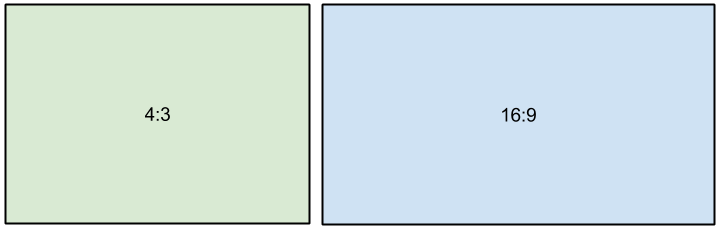
A video's aspect ratio is the proportion of its width to height, e.g. 16:9 (read as sixteen-by-nine). Usually, you might encounter the 16:9 or 4:3 aspect ratios, but most recent displays and videos have the 16:9 aspect ratio. You might encounter 4:3 resolutions in some older TV videos. Here's how different they look:
If you join videos with different aspect ratios, you might see black bars around the edges. Think of a video's frame like a box: if you put a square peg into a rectangular hole, you might have room left over at the sides. This can happen in your project if you're mixing videos and photos, or if you're using videos from different sources. This is how it might look if you're adding 4:3 videos to a 16:9 project and vice versa:
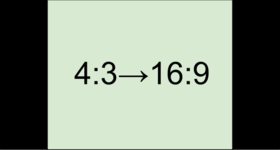

To remove the black bars, try using the crop tool, or change the project settings.
Learn more: Removing black bars
Bitrate
Bitrate is a property of digital video and audio files. It means the amount of data in bits contained in each second of the file. Higher bitrate allows to preserve more detail, but also requires much more disk space for the output file. Bitrate also depends on your video resolution, because you need much more data to store a large HD video frame compared to a tiny 360p video. If your video has lots of small details or fast action, you can choose a higher quality when saving the video. The output video will have a larger file size, but you'll be able to see detail better.
Codec
Video and audio information is processed or encoded to shrink the size of the file. However, your computer needs to have a decoder installed in order to open the file. There are many different codecs, each compressing video in different ways. Many video formats can store multiple video formats. For example, you can save a video with the .mp4 extension, but you can use the H.264 or MPEG-4 codecs. If you don't know what codec works best for you, go for H.264 – it is supported by most players and platforms.
Hint: Don't download codecs from suspicious websites. They may contain malware.
Format
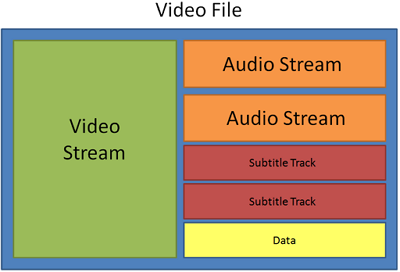
Usually when someone mentions formats, they mean container formats, namely, the way of storing a video or audio file's information inside a file. You can spot container formats by file extensions. A container format contains video and audio streams, that are be encoded with a codec. The figure below shows how a standard video file may look like.
Frame rate, FPS
A video's frame rate is the number of frames or still images in each second of the video (also called FPS or frames per second). Most movies have a frame rate of 24 frames per second, but most cameras and mobile phones shoot video at 30 frames per second. More modern cameras even allow you to film with 60 FPS and above. If you have a higher frame rate, you can slow down the video to make a slow-motion effect without making the video look choppy.
*.mepx files
Movavi Academic project files are saved with the MEPX extension. You can open the file in the Editor and continue working on your project.
A video's resolution is basically its width and height in pixels. Usually it is written as the width multiplied by height, e.g. "1280x720", or sometimes you might only see the height listed, e.g. "720p". Usually, videos with high resolution have better quality because there are more pixels available for storing information. However, if you convert a low-quality video to a higher resolution, it will not instantly look better because there is nowhere to restore the extra information from, so you will end up with the same quality with a much larger file size. You can change the resolution of your output video in project settings.
Sample rate
The sample rate affects the quality of digital sound, and defines the maximum frequencies that an audio stream can contain. The default sample rate is set to 44100 Hz, which exceeds the maximum frequencies of human hearing and is used to record Audio CDs and most music tracks.
Stream
A video file contains the video and audio information in separate streams, which simply means that their data is stored separately inside the file. When you play the file, these streams are played simultaneously, just like a stream of water.