| Movavi Slideshow Creator :: Format reference
:: MPEG (DVD, VCD, SVCD)
|
MPEG Video Format
MPEG is a short for Moving Picture Experts Group, is the
name of familly of standards used for coding audio and video data
in a digital compressed format including data transmission across
digital networks. MPEG Video files have the .mpg or
.dat extension and MPEG Audio files generally have
the extension .mp1, .mp2, .mp3. MPEG is cross-platform
compatible and can be played on all popular computer systems.
Decoding and playing an MPEG file is generally harder on
system resources than decoding and playing an AVI file, a factor
that makes choosing the correct media type very important.
MPEG-1 Media Type files are generally easier on system
resources and smaller in file size than other MPEG Media Types. An
issue that must be considered when selecting an MPEG Media Type is
the CPU speed of the system that will play your videos. For
example, even slightly older Pentium systems (such as those with
CPU speeds under 350 - 450 MHz) cannot reliably decode and play the
MPEG-2 media type. However, MPEG-1 can be decoded and played on
just about any Pentium (or generic Pentium) computer. Playing MPEGs
on 486 machines is possible, but special software, and at times
special hardware (depending on the system setup) is required.
MPEG-2 is a newer, more flexible, and more powerful MPEG
Media Type. The quality of MPEG-2 can be so good that it's the file
format used in DVD and digital satellite television. The most
significant downside of MPEG-2 in terms of use on the Internet is
system resources: MPEG-2 requires at least a Pentium 350 - 450 (or
generic Pentium 350 - 450) CPU for reliable decoding and
playback.
MPEG-4 is designed to deliver DVD (MPEG-2) quality video
at lower data rates and smaller file sizes. While audio and video
are at the core of the MPEG-4 specification, MPEG-4 can also
support 3D objects, sprites, text and other media types. MPEG-4
allows the use of different encoding methods, for instance a
keyframe can be encoded using ICT or Wavelets resulting in
different output qualities.
MPG can be either an abbreviation for MPEG or is used as
a file extension for MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 video data.
Use MPEG Presets - DVD, VCD, SVCD PAL/NTSC Compatible - for
converting your video to DVD, VCD, SVCD compatible formats.
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) is DVD-Video recorded on a
DVD-R or DVD-RW disc, which contains superior quality video
(MPEG-2) and audio. Typically, a DVD can hold more than one hour of
video.
DVD Video Parameter Settings
- Frame Size: 720x480 (NTSC) or 720x576 (PAL)
- Frame Rate: 29.97 frames/second (NTSC) or 25
frames/second (PAL)
- Video Data Rate: 4~8 Mbps CBR or VBR
(Constant/Variable Bit Rate)
- Audio Settings: Stereo, 48 kHz and 192~384 kbps
MPEG audio
DVD Playback Options:
- Stand-alone DVD players
- Computer DVD drives with playback software
VCD (Video Compact Disc)is a CD-ROM disc that contains
video and audio. Typically, a VCD can hold about 74 minutes (650MB)
of video and stereo-quality audio. The video and audio are stored
in MPEG-1 format and follow certain standards (White Book). VCD
video quality is roughly the same as VHS video.
VCD Video Parameters Settings
- Frame Size: 352x240 (NTSC) or 352x288 (PAL)
- Frame Rate: 29.97 frames/second (NTSC) or 25
frames/second (PAL)
- Video Data Rate: 1152 kbps
- Audio Settings: Stereo, 44.1kHz and 224kbps audio
bit rate
VCD Playback Options:
- Almost all stand-alone VCD or DVD Players with CD-R
or CD-RW playback capabilities (See DVD player manufacturer for
compatibility)
- Computer DVD/CD-ROM drives with playback
software
SVCD (Super Video Compact Disc) is a CD-ROM disc that
contains high quality video and audio. Typically, a SVCD can hold
about 35~45 minutes (650MB) of video and stereo-quality audio
(depends on the data rate used for encoding). The video and audio
are stored in MPEG-2 format, much like a DVD. SVCD video has better
quality than VHS video.
SVCD Video Parameter Settings
- Frame Size: 480x480 (NTSC) or 480x576 (PAL)
- Frame Rate: 29.97 frames/second (NTSC) or 25
frames/second (PAL)
- Video Data Rate: Variable bit rate up to 2600
kbps
- Audio Settings: 32~384 kbps MPEG-1 Layer 2 audio
bit rate
NOTE: The maximum audio and video combined data rate
cannot exceed 2750kbps.
SVCD Playback Options:
- Some stand-alone DVD Players with CD-R or CD-RW
playback capabilities (See DVD player manufacturer for
compatibility)
- Computer DVD/CD-ROM drives with playback
software
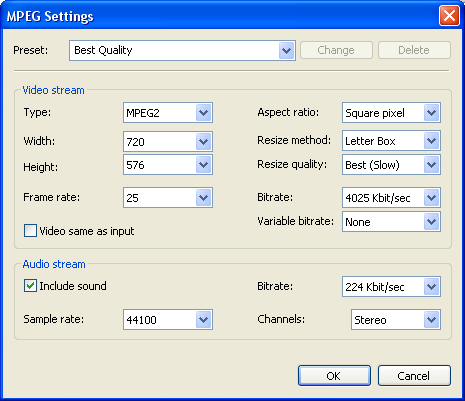
MPEG Format Settings
- Specify a type of MPEG compression to use: MPEG1 or
MPEG2.
- Specify the Bitrate. The larger values produce higher
quality.
- If needed, enter new values for Width and Height
of your video. The dimensions are in pixels. Check Link of width
and weight to constrain the proportions. Check Biquadratic
approximation resizing for more precize resizing method,
resulting in the better picture quality.
- If needed, enter a new value for Frames per Second.
Larger values produce "softer" videos but require more system
resources.
- Check Include a Sound to record an audio stream into the
file. Choose Audio format, frequency and Channels (Mono or
Stereo). The larger values provide better quality.
Back to the list of formats
© MOVAVI
|
